-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 21
Configuration
The configuration of CoreScope is twofold. The gNodeB is configured via the configuration file, while the UEs can be configured via runtime via a Web API. Both steps are described in the following.
To configure CoreScope's gNodeB changes need to be made to the configuration file. The AMF, N1C and GTP addresses need to be changed, as well as the PLMN and TAC.
First, copy the configuration file to your home folder:
corescope$ mkdir -p $HOME/.config/srsran
corescope$ cp ./corescope/corescope.conf.example $HOME/.config/srsran/corescope.conf
The following addresses should be used for the AMF, N1C and GTP:
- AMF: Outgoing IP of VM (e.g. 192.168.56.101)
- N1C: IP of VM host-only adapter on local machine (e.g. 192.168.56.1)
- GTP: IP of VM host-only adapter on local machine (e.g. 192.168.56.1)
Note:
You can find these values using ifconfig and taking the IPs from the relevant network adapters.
The PLMN and TAC also need to be changed in the config file to match the values used in the Core. The following uses example values.
- TAC: 0x01
- MCC: 901
- MNC: 70
The CoreScope configuration file should then look like the following:
#####################################################################
[gnb]
gnb_id = 0x19B
name = "srsgnb"
cell_id = 0x01
tac = 0x01
mcc = 901
mnc = 70
amf_addr = 192.168.56.101
gtp_bind_addr = 192.168.56.1
n1c_bind_addr = 192.168.56.1
#####################################################################
UEs are created via the API (OpenAPI), which is provided by CoreScope on localhost:8000. For more information see the API description .
An example test script for spawning UEs can be found here:
/$HOME/corescope/examples/corescope-api-client/corescope-tester.py.
Using this script is outlined further in this application note.
CoreScope provides you with an API that on can be launched on localhost:8000. This allows users to explore the complete functionality of CoreScope and view live reports of metrics. Different methods can be used to access the API.
CoreScope has an integrated Web UI through the use of OAT++ and the Swagger module.
It can be accessed via your web browser by visiting
http://localhost:8000/swagger/ui while CoreScope is running.
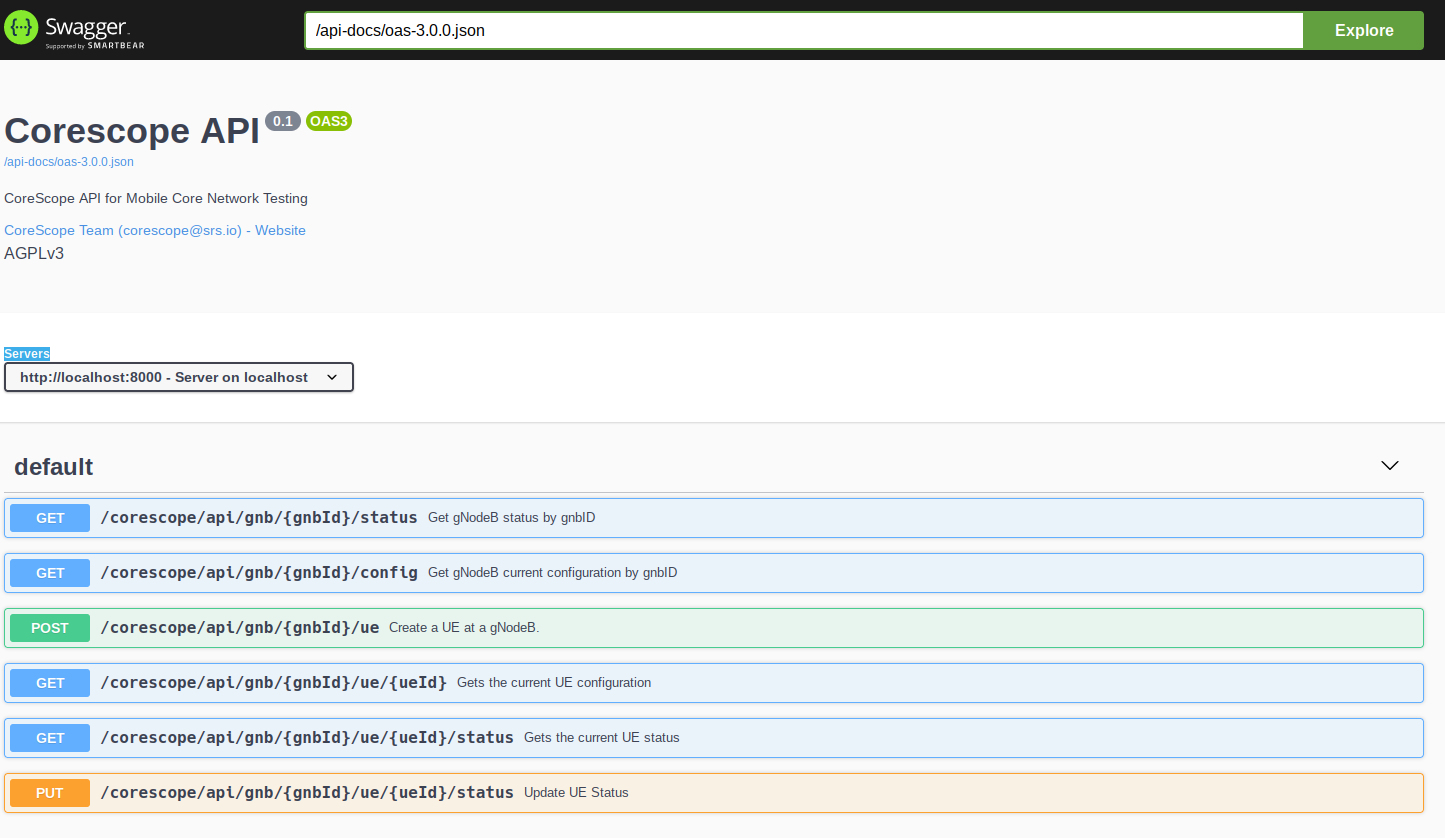
The following functions are currently supported:
- GET/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/status => Get gNodeB status by gnbID
- GET/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/config => Get gNodeB current configuration by gnbID
- POST/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/ue => Create a UE at a gNodeB.
- GET/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/ue/{ueId} => Gets the current UE configuration
- GET/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/ue/{ueId}/status => Gets the current UE status
- PUT/corescope/api/gnb/{gnbId}/ue/{ueId}/status => Update UE Status (Switch on and off)
When you launch the UI you should see the following:
Python API for CoreScope can be generated with the openapi-python-client.
With CoreScope running, the following command can be used to generate the code:
openapi-python-client generate --url http://localhost:8000/api-docs/oas-3.0.0.json
This API code is already provided in the
/corescope/examples/corescope-api-client folder.
These applications can be used to spawn UEs and gNBs while CoreScope is running to exercise the core as per the users needs.