Quickly create customizable UI components around your models. Gradio makes it easy for you to "play around" with your model in your browser by dragging-and-dropping in your own images, pasting your own text, recording your own voice, etc. and seeing what the model outputs.
Gradio is useful for:
-
Demoing your machine learning models for clients / collaborators / users / students
-
Deploying your models quickly with automatic shareable links and getting feedback on model performance
-
Debugging your model interactively during development using built-in interpretation visualizations for any model
You can find an interactive version of the following Getting Started at https://gradio.app/getting_started.
To get Gradio running with a simple example, follow these three steps:
1. Install Gradio from pip.
pip install gradio2. Run the code below as a Python script or in a Python notebook (or in a colab notebook).
import gradio as gr
def greet(name):
return "Hello " + name + "!!"
iface = gr.Interface(fn=greet, inputs="text", outputs="text")
iface.launch()3. The interface below will appear automatically within the Python notebook, or pop in a browser on http://localhost:7860 if running from a script.
Gradio can wrap almost any Python function with an easy-to-use user interface. That function could be anything from a simple tax calculator to a pretrained machine learning model.
The core Interface class is initialized with three parameters:
fn: the function to wrapinputs: the input component type(s)outputs: the output component type(s)
With these three arguments, we can quickly create interfaces and launch() them. But what if you want to change how the UI components look or behave?
Let's say we want to customize the input text field - for example, we wanted it to be larger and have a text hint. If we use the actual input class for Textbox instead of using the string shortcut, we have access to much more customizability. To see a list of all the components we support and how you can customize them, check out the Docs.
import gradio as gr
def greet(name):
return "Hello " + name + "!"
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(lines=2, placeholder="Name Here..."),
outputs="text")
iface.launch()Let's say we had a much more complex function, with multiple inputs and outputs. In the example below, we have a function that takes a string, boolean, and number, and returns a string and number. Take a look how we pass a list of input and output components.
import gradio as gr
def greet(name, is_morning, temperature):
salutation = "Good morning" if is_morning else "Good evening"
greeting = "%s %s. It is %s degrees today" % (
salutation, name, temperature)
celsius = (temperature - 32) * 5 / 9
return greeting, round(celsius, 2)
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=["text", "checkbox", gr.inputs.Slider(0, 100)],
outputs=["text", "number"])
iface.launch()We simply wrap the components in a list. Each component in the inputs list corresponds to one of the parameters of the function, in order. Each component in the outputs list corresponds to one of the values returned by the function, again in order.
Let's try an image-to-image function. When using the Image component, your function will receive a numpy array of your specified size, with the shape (width, height, 3), where the last dimension represents the RGB values. We'll return an image as well in the form of a numpy array.
import gradio as gr
import numpy as np
def sepia(input_img):
sepia_filter = np.array([[.393, .769, .189],
[.349, .686, .168],
[.272, .534, .131]])
sepia_img = input_img.dot(sepia_filter.T)
sepia_img /= sepia_img.max()
return sepia_img
iface = gr.Interface(sepia, gr.inputs.Image(shape=(200, 200)), "image")
iface.launch()Additionally, our Image input interface comes with an 'edit' button which opens tools for cropping, flipping, rotating, drawing over, and applying filters to images. We've found that manipulating images in this way will often reveal hidden flaws in a model.
In addition to images, Gradio supports other media input types, such as audio or video uploads, as well as many output components. Read about these in the Docs.
You can use Gradio to support inputs and outputs from your typical data libraries, such as numpy arrays, pandas dataframes, and plotly graphs. Take a look at the demo below (ignore the complicated data manipulation in the function!)
import gradio as gr
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sales_projections(employee_data):
sales_data = employee_data.iloc[:, 1:4].astype("int").to_numpy()
regression_values = np.apply_along_axis(lambda row:
np.array(np.poly1d(np.polyfit([0,1,2], row, 2))), 0, sales_data)
projected_months = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(
np.arange(3,12), 0), len(sales_data), axis=0)
projected_values = np.array([
month * month * regression[0] + month * regression[1] + regression[2]
for month, regression in zip(projected_months, regression_values)])
plt.plot(projected_values.T)
plt.legend(employee_data["Name"])
return employee_data, plt.gcf(), regression_values
iface = gr.Interface(sales_projections,
gr.inputs.Dataframe(
headers=["Name", "Jan Sales", "Feb Sales", "Mar Sales"],
default=[["Jon", 12, 14, 18], ["Alice", 14, 17, 2], ["Sana", 8, 9.5, 12]]
),
[
"dataframe",
"plot",
"numpy"
],
description="Enter sales figures for employees to predict sales trajectory over year."
)
iface.launch()You can provide example data that a user can easily load into the model. This can be helpful to demonstrate the types of inputs the model expects, as well as to provide a way to explore your dataset in conjunction with your model. To load example data, you provide a nested list to the examples= keyword argument of the Interface constructor. Each sublist within the outer list represents a data sample, and each element within the sublist represents an input for each input component. The format of example data for each component is specified in the Docs.
import gradio as gr
def calculator(num1, operation, num2):
if operation == "add":
return num1 + num2
elif operation == "subtract":
return num1 - num2
elif operation == "multiply":
return num1 * num2
elif operation == "divide":
return num1 / num2
iface = gr.Interface(calculator,
["number", gr.inputs.Radio(["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]), "number"],
"number",
examples=[
[5, "add", 3],
[4, "divide", 2],
[-4, "multiply", 2.5],
[0, "subtract", 1.2],
],
title="test calculator",
description="heres a sample toy calculator. enjoy!",
flagging_options=["this", "or", "that"],
)
iface.launch()You can load a large dataset into the examples to browse and interact with the dataset through Gradio. The examples will be automatically paginated (you can configure this through the examples_per_page argument of Interface) and you can use CTRL + arrow keys to navigate through the examples quickly.
You can make interfaces automatically refresh by setting live=True in the interface. Now the interface will recalculate as soon as the user input changes.
import gradio as gr
def calculator(num1, operation, num2):
if operation == "add":
return num1 + num2
elif operation == "subtract":
return num1 - num2
elif operation == "multiply":
return num1 * num2
elif operation == "divide":
return num1 / num2
iface = gr.Interface(calculator,
["number", gr.inputs.Radio(["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]), "number"],
"number",
live=True
)
iface.launch()Note there is no submit button, because the interface resubmits automatically on change.
Your function may use data that persists beyond a single function call. If the data is something accessible to all function calls, you can create a global variable outside the function call and access it inside the function. For example, you may load a large model outside the function and use it inside the function so that every function call does not need to reload the model.
Another type of data persistence Gradio supports is session state, where data persists across multiple submits within a page load. To store data with this permanence, use gr.get_state and gr.set_state methods.
import gradio as gr
import random
def chat(message):
history = gr.get_state() or []
if message.startswith("How many"):
response = random.randint(1,10)
elif message.startswith("How"):
response = random.choice(["Great", "Good", "Okay", "Bad"])
elif message.startswith("Where"):
response = random.choice(["Here", "There", "Somewhere"])
else:
response = "I don't know"
history.append((message, response))
gr.set_state(history)
html = "<div class='chatbot'>"
for user_msg, resp_msg in history:
html += f"<div class='user_msg'>{user_msg}</div>"
html += f"<div class='resp_msg'>{resp_msg}</div>"
html += "</div>"
return html
iface = gr.Interface(chat, "text", "html", css="""
.chatbox {display:flex;flex-direction:column}
.user_msg, .resp_msg {padding:4px;margin-bottom:4px;border-radius:4px;width:80%}
.user_msg {background-color:cornflowerblue;color:white;align-self:start}
.resp_msg {background-color:lightgray;align-self:self-end}
""", allow_screenshot=False, allow_flagging=False)
iface.launch()Notice how the state persists across submits within each page, but the state is not shared between the two pages.
Underneath the output interfaces, there is a button marked "Flag". When a user testing your model sees input with interesting output, such as erroneous or unexpected model behaviour, they can flag the input for the interface creator to review. Within the directory provided by the flagging_dir= argument to the Interface constructor, a CSV file will log the flagged inputs. If the interface involves file data, such as for Image and Audio components, folders will be created to store those flagged data as well.
For example, with the calculator interface shown above, we would have the flagged data stored in the flagged directory shown below:
+-- calculator.py
+-- flagged/
| +-- logs.csv
flagged/logs.csv
num1,operation,num2,Output
5,add,7,12
6,subtract,1.5,4.5
With the sepia interface shown above, we would have the flagged data stored in the flagged directory shown below:
+-- sepia.py
+-- flagged/
| +-- logs.csv
| +-- im/
| | +-- 0.png
| | +-- 1.png
| +-- Output/
| | +-- 0.png
| | +-- 1.png
flagged/logs.csv
im,Output
im/0.png,Output/0.png
im/1.png,Output/1.png
You can review these flagged inputs by manually exploring the flagging directory, or load them into the examples of the Gradio interface by pointing the examples= argument to the flagged directory. If you wish for the user to provide a reason for flagging, you can pass a list of strings to the flagging_options argument of Interface. Users will have to select one of the strings when flagging, which will be saved as an additional column to the CSV.
Interfaces can be easily shared publicly by setting share=True in the launch() method. Like this:
gr.Interface(classify_image, "image", "label").launch(share=True)This generates a public, shareable link that you can send to anybody! When you send this link, the user on the other side can try out the model in their browser. Because the processing happens on your device (as long as your device stays on!), you don't have to worry about any packaging any dependencies. If you're working out of colab notebook, a share link is always automatically created. It usually looks something like this: XXXXX.gradio.app. Although the link is served through a gradio link, we are only a proxy for your local server, and do not store any data sent through the interfaces.
Keep in mind, however, that these links are publicly accessible, meaning that anyone can use your model for prediction! Therefore, make sure not to expose any sensitive information through the functions you write, or allow any critical changes to occur on your device. If you set share=False (the default), only a local link is created, which can be shared by port-forwarding with specific users.
Share links expire after 72 hours. For permanent hosting, see Hosting Gradio Apps on Spaces below.
Huggingface provides the infrastructure to permanently host your Gradio model on the internet, for free! You can either drag and drop a folder containing your Gradio model and all related files, or you can point HF Spaces to your Git repository and HP Spaces will pull the Gradio interface from there. See Huggingface Spaces for more information.
Here, we go through several advanced functionalities that your Gradio demo can include without you needing to write much more code!
You may wish to put an authentication page in front of your interface to limit who can open your interface. With the auth= keyword argument in the launch() method, you can pass a list of acceptable username/password tuples; or, for more complex authentication handling, you can even pass a function that takes a username and password as arguments, and returns True to allow authentication, False otherwise. Here's an example that provides password-based authentication for a single user named "admin":
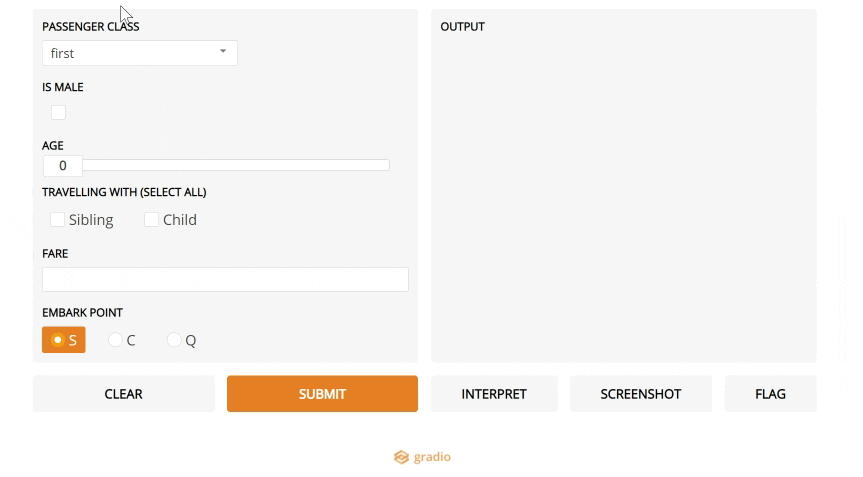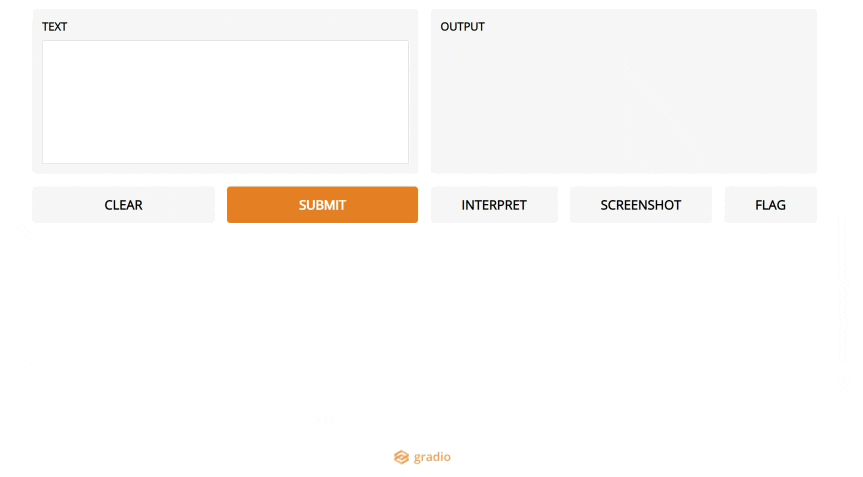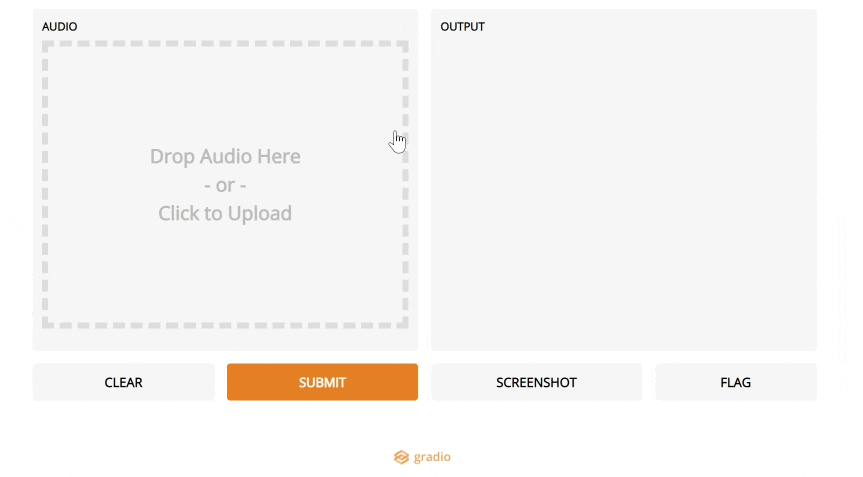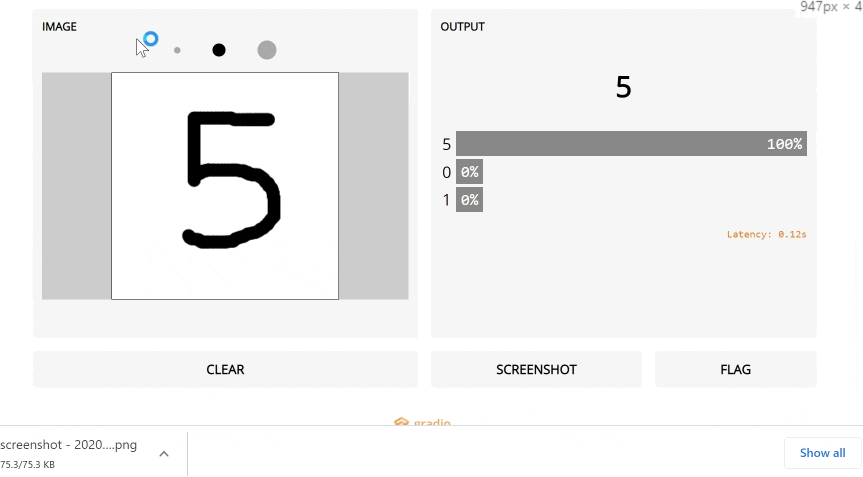
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label).launch(auth=("admin", "pass1234"))Most models are black boxes such that the internal logic of the function is hidden from the end user. To encourage transparency, we've made it very easy to add interpretation to your model by simply setting the interpretation keyword in the Interface class to default. This allows your users to understand what parts of the input are responsible for the output. Take a look at the simple interface below which shows an image classifier that also includes interpretation:
import gradio as gr
import tensorflow as tf
import requests
inception_net = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2() # load the model
# Download human-readable labels for ImageNet.
response = requests.get("https://git.io/JJkYN")
labels = response.text.split("\n")
def classify_image(inp):
inp = inp.reshape((-1, 224, 224, 3))
inp = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2.preprocess_input(inp)
prediction = inception_net.predict(inp).flatten()
return {labels[i]: float(prediction[i]) for i in range(1000)}
image = gr.inputs.Image(shape=(224, 224))
label = gr.outputs.Label(num_top_classes=3)
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label, interpretation="default").launch()In addition to default, Gradio also includes Shapley-based interpretation, which provides more accurate interpretations, albeit usually with a slower runtime. To use this, simply set the interpretation parameter to "shap" (note: also make sure the python package shap is installed). Optionally, you can modify the the num_shap parameter, which controls the tradeoff between accuracy and runtime (increasing this value generally increases accuracy). Here is an example:
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label, interpretation="shap", num_shap=5).launch()This will work for any function, even if internally, the model is a complex neural network or some other black box. If you use Gradio's default or shap interpretation, the output component must be a Label. All common input components are supported. Here is an example with text input.
import gradio as gr
import re
male_words, female_words = ["he", "his", "him"], ["she", "her"]
def gender_of_sentence(sentence):
male_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in male_words])
female_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in female_words])
total = max(male_count + female_count, 1)
return {"male": male_count / total, "female": female_count / total}
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=gender_of_sentence, inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(default="She went to his house to get her keys."),
outputs="label", interpretation="default")
iface.launch()So what is happening under the hood? With these interpretation methods, Gradio runs the prediction multiple times with modified versions of the input. Based on the results, you'll see that the interface automatically highlights the parts of the text (or image, etc.) that contributed increased the likelihood of the class as red. The intensity of color corresponds to the importance of that part of the input. The parts that decrease the class confidence are highlighted blue.
You can also write your own interpretation function. The demo below adds custom interpretation to the previous demo. This function will take the same inputs as the main wrapped function. The output of this interpretation function will be used to highlight the input of each input interface - therefore the number of outputs here corresponds to the number of input interfaces. To see the format for interpretation for each input interface, check the Docs.
import gradio as gr
import re
male_words, female_words = ["he", "his", "him"], ["she", "her"]
def gender_of_sentence(sentence):
male_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in male_words])
female_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in female_words])
total = max(male_count + female_count, 1)
return {"male": male_count / total, "female": female_count / total}
def interpret_gender(sentence):
result = gender_of_sentence(sentence)
is_male = result["male"] > result["female"]
interpretation = []
for word in re.split('( )', sentence):
score = 0
token = word.lower()
if (is_male and token in male_words) or (not is_male and token in female_words):
score = 1
elif (is_male and token in female_words) or (not is_male and token in male_words):
score = -1
interpretation.append((word, score))
return interpretation
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=gender_of_sentence, inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(default="She went to his house to get her keys."),
outputs="label", interpretation=interpret_gender, enable_queue=True)
iface.launch()If you'd like to change how your interface looks, you can select a different theme by simply passing in the theme parameter, like so:
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label, theme="huggingface").launch()Here are the themes we currently support: "default", "huggingface", "grass", "peach", and the dark themes corresponding to each of these: "darkdefault", "darkhuggingface", "darkgrass", "darkpeach".
If you'd like to have more fine-grained control over any aspect of the app, you can also write your own css or pass in a css file, with the css parameter of the Interface class.
In some cases, you might like to provide your users or testers with more than just a binary option to flag a sample. You can provide flagging_options that they select from a dropdown each time they click the flag button. This lets them provide additional feedback every time they flag a sample.
Here's an example:
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label, flagging_options=["incorrect", "ambiguous", "offensive", "other"]).launch()Gradio integrates nicely with the Hugging Face Hub, allowing you to load models and Spaces with just one line of code. To use this, simply use the load() method in the Interface class. So:
- To load any model from the Hugging Face Hub and create an interface around it, you pass
"model/"or"huggingface/"followed by the model name, like these examples:
gr.Interface.load("huggingface/gpt-2").launch();gr.Interface.load("huggingface/EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B",
inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(lines=5, label="Input Text") # customizes the input component
).launch()- To load any Space from the Hugging Face Hub and recreate it locally (so that you can customize the inputs and outputs for example), you pass
"spaces/"followed by the model name:
gr.Interface.load("spaces/eugenesiow/remove-bg", inputs="webcam", title="Remove your webcam background!").launch()One of the great things about loading Hugging Face models or spaces using Gradio is that you can then immediately use the resulting Interface object just like function in your Python code (this works for every type of model/space: text, images, audio, video, and even multimodal models):
io = gr.Interface.load("models/EleutherAI/gpt-neo-2.7B")
io("It was the best of times") # outputs model completionGradio also lets you mix interfaces very easily using the gradio.Parallel and gradio.Series classes. Parallel lets you put two similar models (if they have the same input type) in parallel to compare model predictions:
generator1 = gr.Interface.load("huggingface/gpt2")
generator2 = gr.Interface.load("huggingface/EleutherAI/gpt-neo-2.7B")
generator3 = gr.Interface.load("huggingface/EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B")
gr.Parallel(generator1, generator2, generator3).launch()Series lets you put models and spaces in series, piping the output of one model into the input of the next model.
generator = gr.Interface.load("huggingface/gpt2")
translator = gr.Interface.load("huggingface/t5-small")
gr.Series(generator, translator).launch() # this demo generates text, then translates it to German, and outputs the final result.And of course, you can also mix Parallel and Series together whenever that makes sense!
If many people are using your interface or if the inference time of your function is long (> 1min), simply set the enable_queue parameter in the Interface class to True to prevent timeouts.
gr.Interface(fn=classify_image, inputs=image, outputs=label, enable_queue=True).launch()This sets up a queue of workers to handle the predictions and return the response to the front end. This is strongly recommended if you are planning on uploading your demo to Hugging Face Spaces (as described above) so that you can manage a large number of users simultaneously using your demo.
If you would like to contribute and your contribution is small, you can directly open a pull request (PR). If you would like to contribute a larger feature, we recommend first creating an issue with a proposed design for discussion. Please see our contributing guidelines for more info.
Gradio is licensed under the Apache License 2.0
You can find many more examples as well as more info on usage on our website: www.gradio.app
See, also, the accompanying paper: "Gradio: Hassle-Free Sharing and Testing of ML Models in the Wild", ICML HILL 2019, and please use the citation below.
@article{abid2019gradio,
title={Gradio: Hassle-Free Sharing and Testing of ML Models in the Wild},
author={Abid, Abubakar and Abdalla, Ali and Abid, Ali and Khan, Dawood and Alfozan, Abdulrahman and Zou, James},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02569},
year={2019}
}