This repository contains a PyTorch implementation of the albert model from the paper
A Lite Bert For Self-Supervised Learning Language Representations
by Zhenzhong Lan. Mingda Chen....
arxiv: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.11942.pdf
-
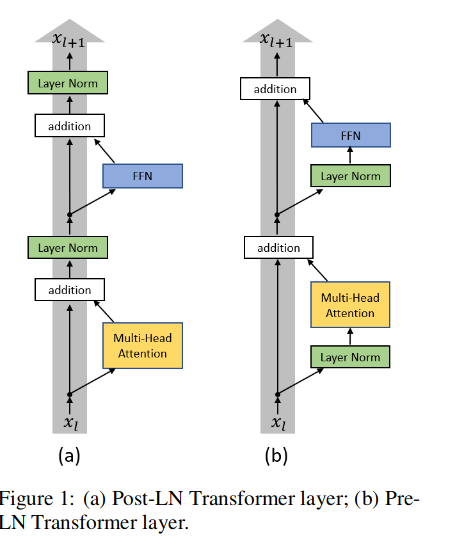
Post-LN: . In the original Transformer, after Layer Norm followed Residual, we called this Post-LN Transformer
-
Pre-LN: Change the position of Layer Norm, for example in the process of Residual (called Pre-LN Transformer)
paper: On Layer Normalization in the Transformer Architecture
How to use
According to the model weight file provided by [brightmart] (https://github.com/brightmart/albert_zh), you need to add the ln_type parameter to the configuration file, as follows:
{
"attention_probs_dropout_prob": 0.0,
"directionality": "bidi",
"hidden_act": "gelu",
"hidden_dropout_prob": 0.0,
"hidden_size": 768,
"embedding_size": 128,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"intermediate_size": 3072 ,
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
"num_attention_heads": 12,
"num_hidden_layers": 12,
"pooler_fc_size": 768,
"pooler_num_attention_heads": 12,
"pooler_num_fc_layers": 3,
"pooler_size_per_head": 128,
"pooler_type": "first_token_transform",
"type_vocab_size": 2,
"vocab_size": 21128,
"ln_type":"postln" # postln or preln
}Cross-Layer Parameter Sharing: ALBERT use cross-layer parameter sharing in Attention and FFN(FeedForward Network) to reduce number of parameter.
modify the share_type parameter:
- all: attention and FFN layer parameters are shared
- ffn: only share FFN layer parameters
- attention: only share the attention layer parameter
- None: No parameter sharing
How to use
When loading config, specify the share_type parameter as follows:
config = BertConfig.from_pretrained(bert_config_file,share_type=share_type)Thanks to Brightmart for providing Chinese model weights: github
-
albert_large_zh Parameter quantity, number of layers 24, size 64M
-
[albert_base_zh (small model experience version)] (https://storage.googleapis.com/albert_zh/albert_base_zh.zip), parameter quantity 12M, layer number 12, size 40M
-
albert_xlarge_zh Parameter size, layer 24, file size 230M
n-gram: The original paper randomly generates n-grams according to the following distribution, the default max_n is 3
-
Convert text data into a one-line, one-sentence format, and use
\nto split between different documents -
Run
python prepare_lm_data_ngram.py --do_datato generate the ngram mask format data set respectively. -
Run
python run_pretraining.py --share_type=allfor model pre-training
Model size
The following is the result of an experiment with bert-base
| embedding_size | share_type | model_size |
|---|---|---|
| 768 | None | 476.5M |
| 768 | attention | 372.4M |
| 768 | ffn | 268.6M |
| 768 | all | 164.6M |
| 128 | None | 369.1M |
| 128 | attention | 265.1M |
| 128 | ffn | 161.2M |
| 128 | all | 57.2M |
-
Download the pre-trained albert model
-
Run
python convert_albert_tf_checkpoint_to_pytorch.pyto convert the TF model weights to the pytorch model weights (by default shar_type=all) -
Download the corresponding dataset, such as the [LCQMC] (https://drive.google.com/open?id=1HXYMqsXjmA5uIfu_SFqP7r_vZZG-m_H0) dataset, which contains training, validation, and test sets. The training set contains 240,000 colloquial descriptions of Chinese. Sentence pairs, the label is 1 or 0. 1 is semantically similar to sentences, and 0 is semantically dissimilar.
-
Run
python run_classifier.py --do_trainfor Fine-tuning training -
Run
python run_classifier.py --do_testto test evaluation
Question matching language task: LCQMC (Sentence Pair Matching)
| Model | Development Set (Dev) | Test Set (Test) |
|---|---|---|
| ALBERT-zh-base(tf) | 86.4 | 86.3 |
| ALBERT-zh-base(pytorch) | 87.4 | 86.4 |