-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 53
checkpoint_09
Two cylindrical resistors are made from the same material and are equal in length. The first resistor has diameter [d], and the second resistor has diameter [2 d].
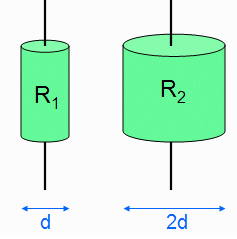
If the same current flows through both, compare the voltage across the two resistors:
- [V_1 > V_2]
Two cylindrical resistors are made from the same material and are equal in diameter. The first resistor has length [L], and the second resistor has length [2 L].

If the same current flows through both, compare the voltage across the two resistors:
- [V_1 < V_2]
Three resistors are connected to a battery with emf [V] as shown. The resistances of the resistors are all the same, i.e. [R_1 = R2 = R3 = R].

Compare the current through R2 with the current through R3:
- [I_2 = I_3]
Compare the current through R1 with the current through R2:
- [\frac{ I_1}{ I_2} = 2]
Compare the current through R1 with the current through R2:
- [V_2 = V_3 < V]
Compare the the voltage across R1 with the voltage across R2.
- [ V_1 = 2 V_2 = V]
The SAME amount of current [I] passes through three different resistors. [R_2] has twice the cross-sectional area and the same length as [R_1], and [R_3] is three times as long as [R_1] but has the same cross-sectional area as [R_1].
In which case is the CURRENT DENSITY through the resistor the smallest?
- Case 2